How To Submit Websites To Search Engines
How To Submit Websites To Search Engines
Boosting the reach of your website and getting organic traffic requires you to submit websites to search engines. This involves submitting your URL to major search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo through tools like Google Search Console.
This crucial step increases the chances of your site appearing in relevant search results. This guide will enhance your site's discoverability and optimize its search engine presence.

Step 1: Prepare Your Website
Before submitting your website, ensure it meets the following criteria:
1. Mobile-Friendly Design
Ensure your website is fully responsive and adjusts seamlessly to different screen sizes, especially mobile devices. Since most searches are now conducted on smartphones, a mobile-friendly site improves user experience and is vital for higher search engine rankings.
2. Fast Loading Speed
Optimize your website's faster loading times, as slow-loading pages frustrate visitors and increase bounce rates. Search engines prioritize sites with speedy performance, making it essential to use techniques like image compression and efficient coding to enhance speed.
3. SEO Optimization
Integrate relevant keywords naturally throughout your content, and ensure your meta descriptions and title tags are clear and concise.
SEO strategies improve your site’s visibility in search results, attracting more organic traffic and boosting your overall rankings.
Want to Start Making Money Online?
Try My #1 Recommendation Program!
4. Quality Content
Focus on creating original, valuable content that resonates with your audience. Engaging material, such as blog posts, videos, or infographics, keeps users on your site longer and indicates to search engines that your site deserves a higher ranking.
5. Sitemap Creation
To submit your website to search engines, develop and submit a detailed sitemap that outlines its structure. This file helps search engines navigate your site more effectively, ensuring all key pages are indexed and improving visibility and user navigation.
Step 2: Submit Your Website To Google
The most prevalent search engine is Google, so submitting your website here is essential. Follow these steps:
1. Create A Google Search Console Account
To initiate a Google Search Console account, visit the Google Search Console website and sign in with your Google account credentials.
Once logged in, add your website by documenting its URL. This process helps Google understand and index your site, enhancing its visibility in search engine results.
2. Verify Your Ownership
To verify your ownership of Google Search Console, you must confirm that you control the website. Methods for ascertaining this include uploading an HTML file, adding a meta tag to your site's HTML, or verifying through your domain name provider. This step is vital to gaining access to site management tools.
Want to Find Out How To Start Your Home-Based Business?
Try My #1 Recommendation Platform!
3. Submit Your Sitemap
To submit your sitemap in Google Search Console, navigate to the “Sitemaps” section within the tool. Insert the URL of your sitemap, such as https://yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml, into the provided field. After inputting the URL, click“Submit” to notify Google about your website’s structure, ensuring all pages are correctly indexed.
4. Request Indexing
To submit your website to search engines, create and submit a detailed sitemap outlining its structure. This helps search engines index key pages and improves visibility. To request indexing in Google Search Console, use the URL Inspection Tool to verify and submit pages for crawling
Step 3: Submit Your Website To Microsoft Bing
Bing is another significant search engine that should not be overlooked. Here’s how to submit your website:
1. Create A Bing Webmaster Tools Account
To create a Bing Webmaster Tools account, see the Bing Webmaster Tools site and sign in using your Microsoft account credentials.
Once logged in, add your website by inserting its URL and verifying ownership. This enables you to monitor your site’s performance and optimize it for Bing search rankings.
- Visit Bing Webmaster Tools.
- Sign in with your Microsoft account.
2. Add Your Website
Log in to your account first to count your website to Bing Webmaster Tools. Once signed in, find the option to add a new site.
Are You Tired Of Scams?
Want to Start Making Money Online?
Enter your website’s URL into the designated field and select the “Add” button. This process connects your website to Bing’s tools for tracking and optimization.
3. Verify Ownership
To verify ownership in Bing Webmaster Tools, similar to Google, you must confirm that you control the website. This can be done by inserting a meta tag into your website’s HTML, uploading an XML file to your site, or verifying through your DNS provider. This step ensures proper access and management of your site.
4. Submit Your Sitemap
To submit your sitemap in Bing Webmaster Tools, navigate to your account's “Sitemaps” section. Once there, enter the URL of your sitemap (e.g., https://yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml) into the provided field. After entering the URL, click the“Submit” button to notify Bing about your website's structure for better indexing.
Step 4: Submit Your Website To Other Search Engines
Submit your website to search engines by creating and submitting a sitemap for better indexing. Use Google’s URL Inspection Tool for indexing and submit to other search engines to boost visibility and attract diverse traffic.
1. Yahoo
Yahoo's search results are powered by Bing, meaning submitting your website to Bing also ensures it appears in Yahoo search results.
By submitting to Bing, you effectively cover both search engines, boosting your site's visibility on both platforms simultaneously.
2. DuckDuckGo
DuckDuckGo doesn’t offer a direct submission process. It relies on crawling websites through external links. To get your site indexed, focus on acquiring backlinks from reputable sources. This helps DuckDuckGo discover and rank your site's search results over time.
3. Yandex
To submit your website to Yandex, create an account on Yandex Webmaster. Once signed in, add your website by entering its URL and completing the ownership verification process.
Want To Learn How To Create Your Own Website And Online Business?
Try My #1 Recommendation Training And Hosting Platform!
After verification, submit your sitemap to help Yandex crawl and index your website for adequate visibility to Russian audiences.
4. Baidu
When submitting your website to Baidu, you must first obtain a Chinese business license for registration. After creating an account on Baidu Webmaster, verify ownership of your site.
Once verified, submit your sitemap to help Baidu crawl and index your website for adequate visibility among Chinese audiences.
Step 5: Monitor Your Website’s Performance
Submit your website to search engines by creating a sitemap, using Google’s URL Inspection Tool, and monitoring performance with Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools.
1. Check Indexing Status
To check the indexing status of your website, utilize tools like Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools. These platforms show which pages are indexed.
You can also perform a site-specific search (e.g., site:yourwebsite.com) to directly see the pages indexed by search engines.
2. Analyze Traffic
Utilize tools like Google Analytics to track and analyze your website’s traffic. These tools provide valuable data on user behaviour, visitor sources, and conversion rates.
Understanding how users interact with your site can help you make data-driven decisions to enhance performance and optimize user experience, resulting in better results.
3. Fix Errors
Regularly monitor Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools for any crawl errors or warnings related to your website.
Resolve these issues as soon as they appear to ensure that search engines can properly index your site. Fixing errors helps enhance site performance and maintain strong search rankings.
4. Update Content Regularly
Consistently updating your website’s content is essential for retaining search engine rankings and user interest. New, appropriate content indicates search engines that your site is active and authoritative while providing value to visitors. Regular updates can lead to increased engagement and improved rankings over time.
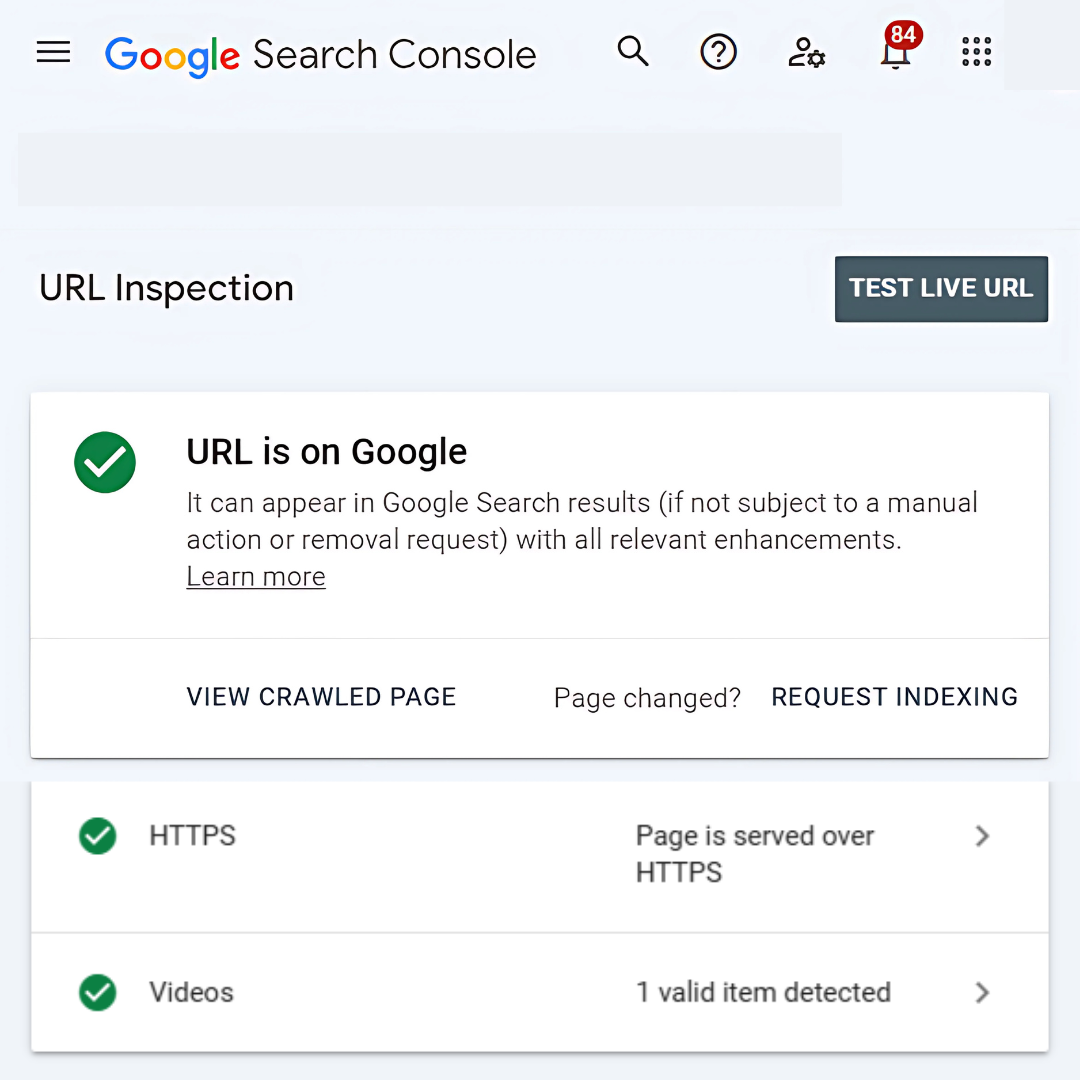
How To Check If A Page Is Indexed
Use Google’s “site:” search operator to check if a page is indexed. Simply type site:yourwebsite.com/page-name in the search bar. If the page appears in the results, it’s indexed by Google.
Submit your website to search engines by creating a sitemap and using Google’s URL Inspection Tool to check the indexing status. Alternatively, use Google Search Console to identify crawl errors or restrictions preventing indexing.
Bing Webmaster Tools also offers a similar feature. By entering the page URL into their diagnostic tools, you can check whether Bing has indexed it, ensuring your content is visible on multiple search engines.
How To Resolve Indexing Problems In Google Search Console
Fixing indexing issues in Google Search Console (GSC) ensures your website is crawled correctly and ranked on Google. Here’s a step-by-step guide to address and resolve common indexing issues:
1. “Discovered – Currently Not Indexed”
“Discovered – Currently Not Indexed” means Google has found the page but hasn’t crawled it yet. This can happen due to low crawl priority or limitations in server resources, preventing the page from being indexed despite its discovery.
How To Fix
To resolve the “Discovered—Currently Not Indexed” issue, focus on improving content quality, enhancing internal linking, requesting manual indexing, and optimizing the crawl budget. These steps ensure that Google indexes your page effectively and prioritizes it over less essential pages.
- Improve content by adding unique, valuable information.
- Add internal links from important pages.
- Use the URL Inspection Tool to request indexing.
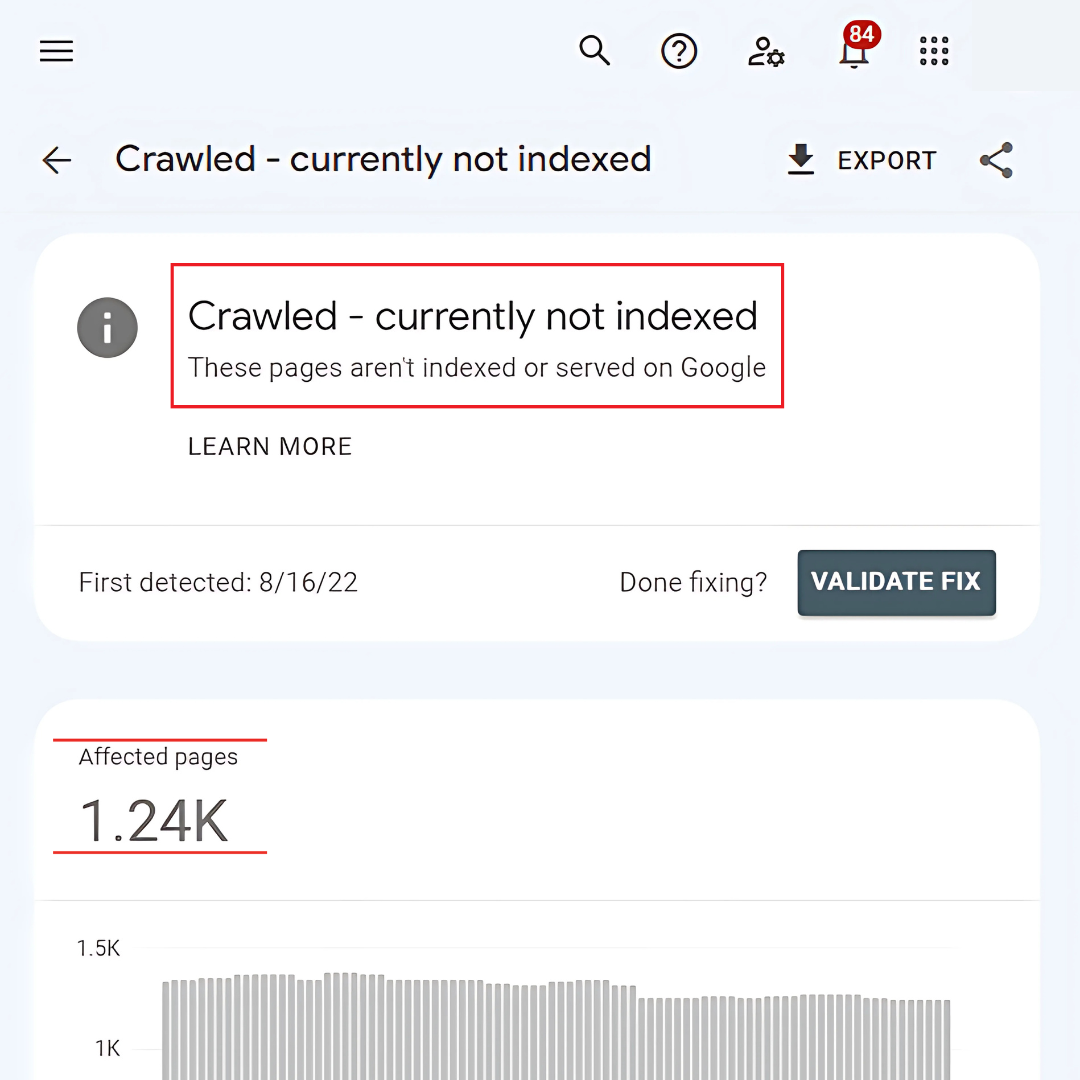
2. “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed”
“Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” means Google crawled the page but chose not to index it. This typically happens due to thin content, duplicate material, or low-quality content that doesn’t meet Google's standards for indexing and ranking in search results.
How To Fix
To fix indexing issues, enhance your content by adding relevant, in-depth, and unique material. Resolve duplicate content using canonical tags, fix metadata issues like titles and descriptions, and resubmit the page through the URL Inspection Tool for reindexing after improvements.
- Add unique, relevant, and detailed content.
- Resolve duplicates with canonical tags or by consolidating pages.
- Ensure proper meta titles and descriptions.
3. “Blocked By Robots.Txt”
“Blocked by robots.txt” means the page is restricted by the rules in the robots.txt file, preventing Googlebot from crawling it. This could be intentional or accidental, as the file can block specific pages from being accessed by search engine crawlers.
How To Fix
To fix the issue of pages being blocked by robots.txt, review the file for any disallowed rules related to the page. Remove or modify the disallow directives, ensuring the page is accessible to search engines and can be crawled and indexed correctly.
- Review robots.txt for rules that are disallowed and affect the page.
- Remove or modify disallow directives.
- Ensure the page is crawlable and accessible.
4. “Excluded By ‘noindex’ Tag”
“Excluded by ‘noindex' Tag” occurs when a meta tag with the value “noindex” is placed on the page, instructing Google not to index it. This prevents you from being able to submit your website to search engines, even though Googlebot crawls it.
How To Fix
To fix issues with a ‘no index’ tag, remove it from the page’s HTML to make it indexable. After making the update, use the URL Inspection Tool to verify the change, then request reindexing through Google Search Console to ensure proper indexing.
- Remove the ‘noindex’ tag from the page’s HTML.
- Use the URL Inspection Tool to verify the page is indexable.
- Request reindexing through Google Search Console.
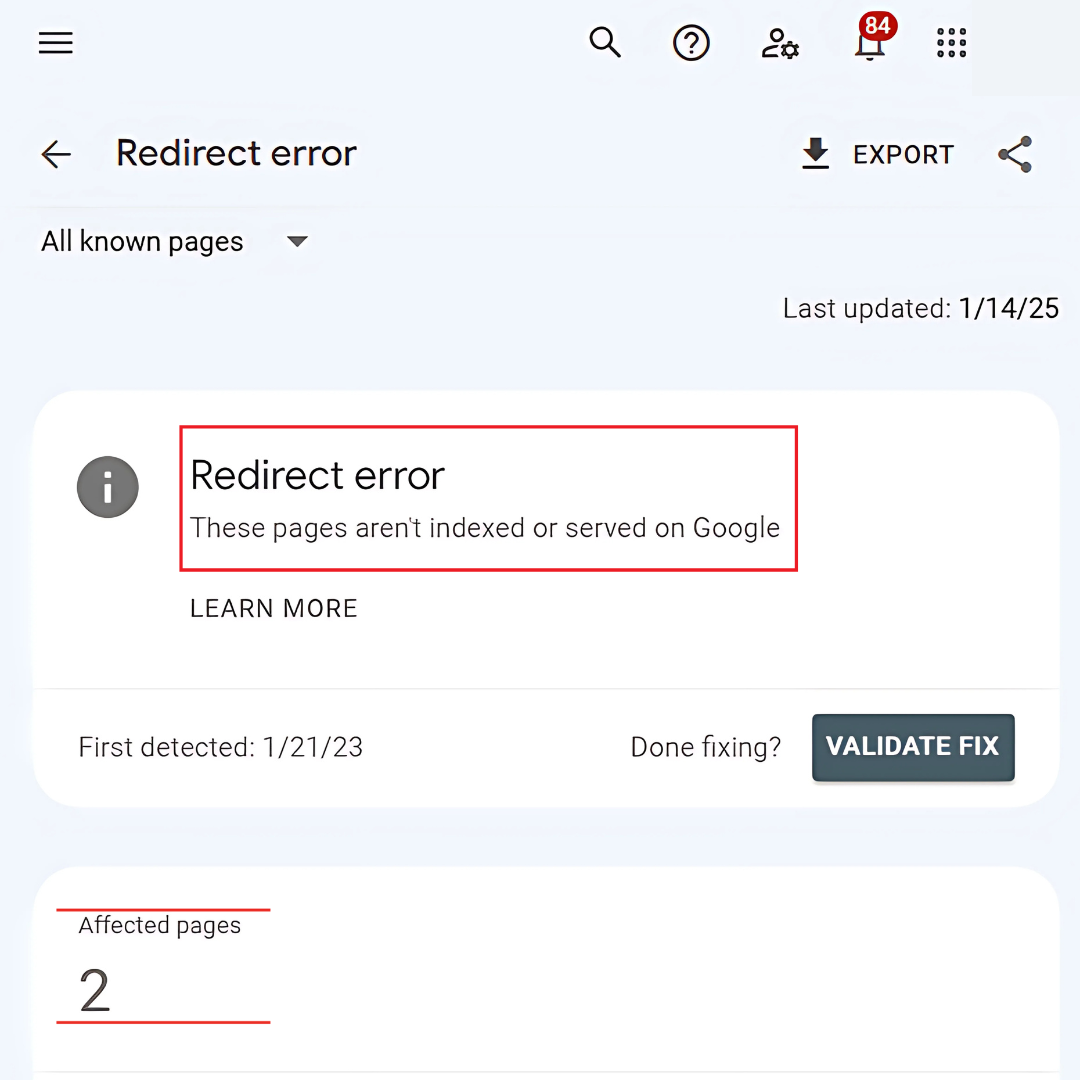
5. “Redirect Error”
“Redirect Error” occurs when there are issues with redirect chains, loops, or incorrect configurations. These problems prevent Google from adequately accessing or indexing the intended page, leading to potential ranking and visibility issues in search results.
How To Fix
To fix redirect issues, ensure all redirects are 301 (permanent) and avoid redirect chains or loops, which can harm SEO. Use Google Search Console’s URL Inspection Tool to test and validate the final destination of redirected URLs for proper indexing.
- Ensure redirects are 301 (permanent) and avoid chains or loops.
- Use the URL Inspection Tool to validate the redirected URL's destination.
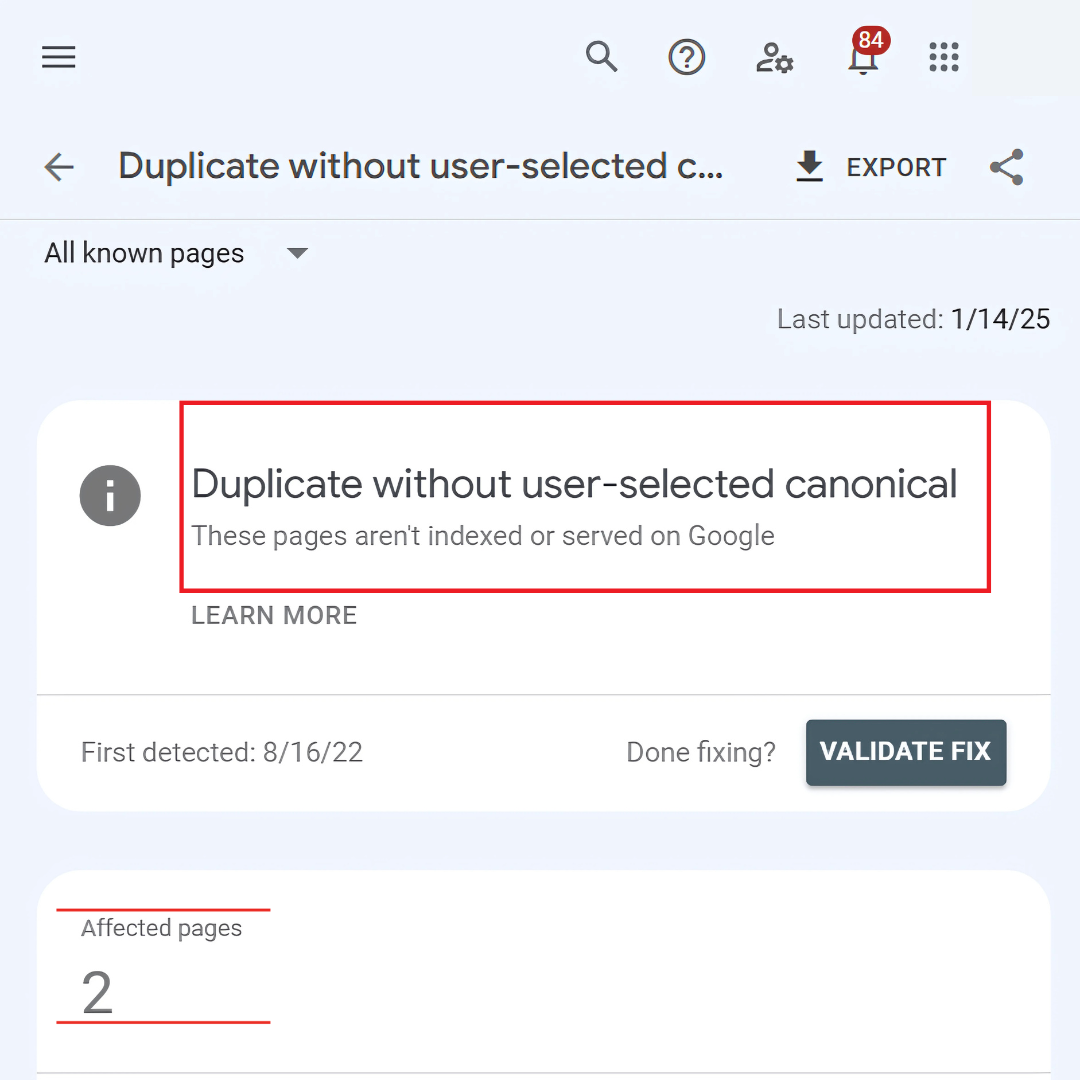
6. “Duplicate Without Canonical Tag”
“Duplicate Without Canonical Tag” means the page is identified as a duplicate of another but lacks a canonical tag to suggest the preferred version. This can confuse search engines, potentially causing them to ignore or misinterpret the page in search results.
How To Fix
To fix duplicate content issues, add a canonical tag to identify the preferred version of the page. Update your sitemap to include only canonical URLs and, if needed, consolidate duplicate pages to avoid confusion and ensure proper indexing.
- Add a canonical tag to specify the preferred version of the page.
- Update the sitemap with canonical URLs.
- Merge duplicate pages to avoid confusion.
7. “Submitted URL Not Found (404)”
It occurs when a URL is submitted to Google, which leads to a 404 error. This typically happens if the page has been deleted or there is an incorrect URL mapping, causing the page to be inaccessible to both users and search engines.
How To Fix
To fix a broken page, restore the deleted page or set up a 301 redirect to a relevant page. Remove the fractured URL from your sitemap to prevent indexing errors, and use the URL Inspection Tool to validate the fix and request reindexing.
- Restore the deleted page or set up a 301 redirect.
- Exclude the broken URL from the sitemap.
- Use the URL Inspection Tool for validation and reindexing.
8. “Soft 404”
“Soft 404” occurs when Google detects a page that appears to be a 404 error but doesn't return the correct HTTP status code. This typically happens when the page has little or no meaningful content, leading Google to treat it as a non-existent page.
How To Fix
To fix indexing issues, ensure the page has relevant, valuable content. Return a proper 404 or 410 HTTP status code if the page doesn't exist. Implement a redirect to a more appropriate, active URL for outdated pages to guide users.
- Add valuable, relevant content to the page.
- Return a proper 404 or 410 status for non-existent pages.
- Redirect outdated pages to relevant URLs.
9. “Server Errors (5xx)”
“Server Errors (5xx)” occurs when the server returns a 5xx status code, indicating a server-side issue. This prevents Google from accessing the page, as it means temporary or permanent server problems, such as server overload, misconfigurations, or downtime.
How To Fix
To fix server-related issues, check server logs to identify the cause, such as overload or configuration problems. Resolve the underlying server configurations and monitor your uptime using tools like Google Cloud Monitoring or UptimeRobot to ensure stable performance.
- Check server logs to identify error causes.
- Fix server configurations to prevent recurring issues.
- Use Google Cloud Monitoring to monitor uptime.
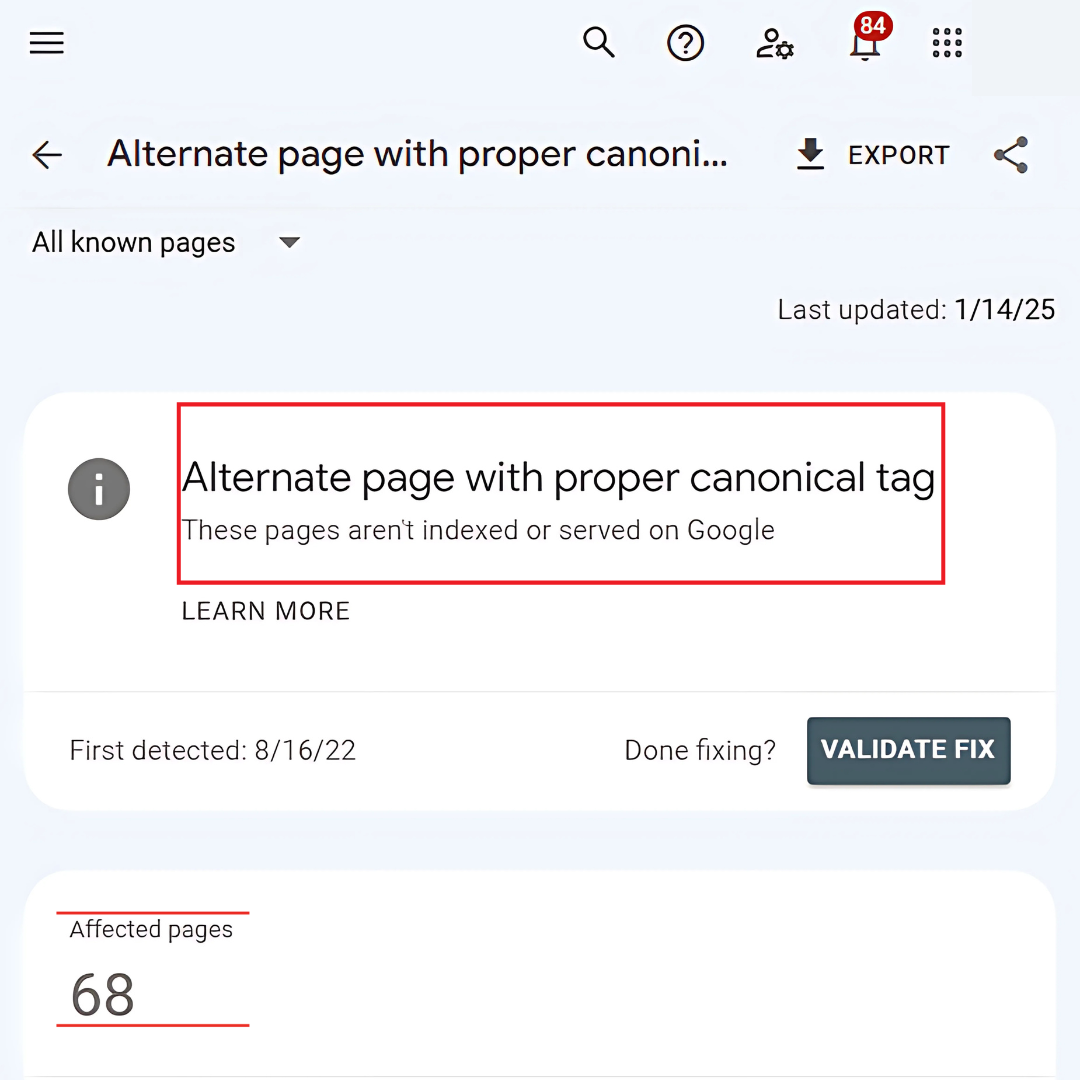
10. “Alternate Page With Proper Canonical Tag”
Submit your website to search engines by creating a sitemap. “Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag” occurs when a page points to another as the canonical version. This signals Google to index the preferred page, avoiding duplicate content and ensuring proper ranking.
How To Fix
To fix issues with canonical tags, review the tag to ensure it correctly points to the intended page. Verify that the canonical URL is indexed and functioning properly by checking its status in Google Search Console or other webmaster tools.
- Review the canonical tag to ensure it points to the correct page.
- Verify that the canonical URL is indexed and functional.
Conclusion
Introducing your website to search engines is crucial in improving its visibility and ensuring it appears in search results.
Boost your website's performance by creating and submitting a sitemap. Use tools like Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools to fix indexing issues.
Monitoring its progress regularly and submitting updates will help attract diverse traffic, improve rankings, and enhance your site’s online presence.
I trust you enjoyed this article on How To Submit Websites To Search Engines. Please stay tuned for more articles to come.
Take care!
JeannetteZ
Want to Learn How to Build Your Own Home-Based Online Business And Start Making Money Online From Your Comfortable Couch?
Try Wealthy Affiliate!
Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I would love to hear from you. Please leave me your questions, experiences, remarks, and suggestions on How To Submit Websites To Search Engines in the comments below. You can also contact me by email at Jeannette@WorkFromAnywhereInTheWorld.com.
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. I earn from qualifying purchases as an Amazon Associate and other affiliate programs. Please read my full affiliate disclosure.
You may also enjoy the following articles:
Wealthy Affiliate Coupons For Premium Memberships
Wealthy Affiliate Review – Scam or Legit? The Truth Exposed
An Insider Wealthy Affiliate Review