The Ultimate Guide To E-Commerce Business Models
In the digital marketplace, e-commerce business models specify how companies function, make money, and provide value to consumers.
From traditional retail models to innovative subscription services, each approach offers unique opportunities and challenges.
Understanding these models helps entrepreneurs choose the right strategy for their goals, target audience, and resources.
In this article, we’ll explore the main types of e-commerce business models, their advantages, and how they shape the ever-evolving world of online commerce.
What Is An E-Commerce Business Model?
An e-commerce business model is the framework that outlines how an online business creates, delivers, and earns revenue from its products or services.
Think of it as the blueprint for your digital store’s success. It defines who your customers are, what you’re offering them, how you’ll market it, and the way transactions will happen.
Businesses that cater to other businesses (B2B) and those that sell directly to consumers (B2C) are two examples. There are also models based on subscriptions, dropshipping, marketplaces, and more—each with its benefits and challenges.
Choosing the right e-commerce business model is crucial because it impacts everything from your pricing strategy to your customer experience.
A well-defined model ensures that your operations run smoothly, marketing efforts are targeted, and revenue streams are sustainable.
Types Of E-Commerce Business Models
Based On Transaction Parties
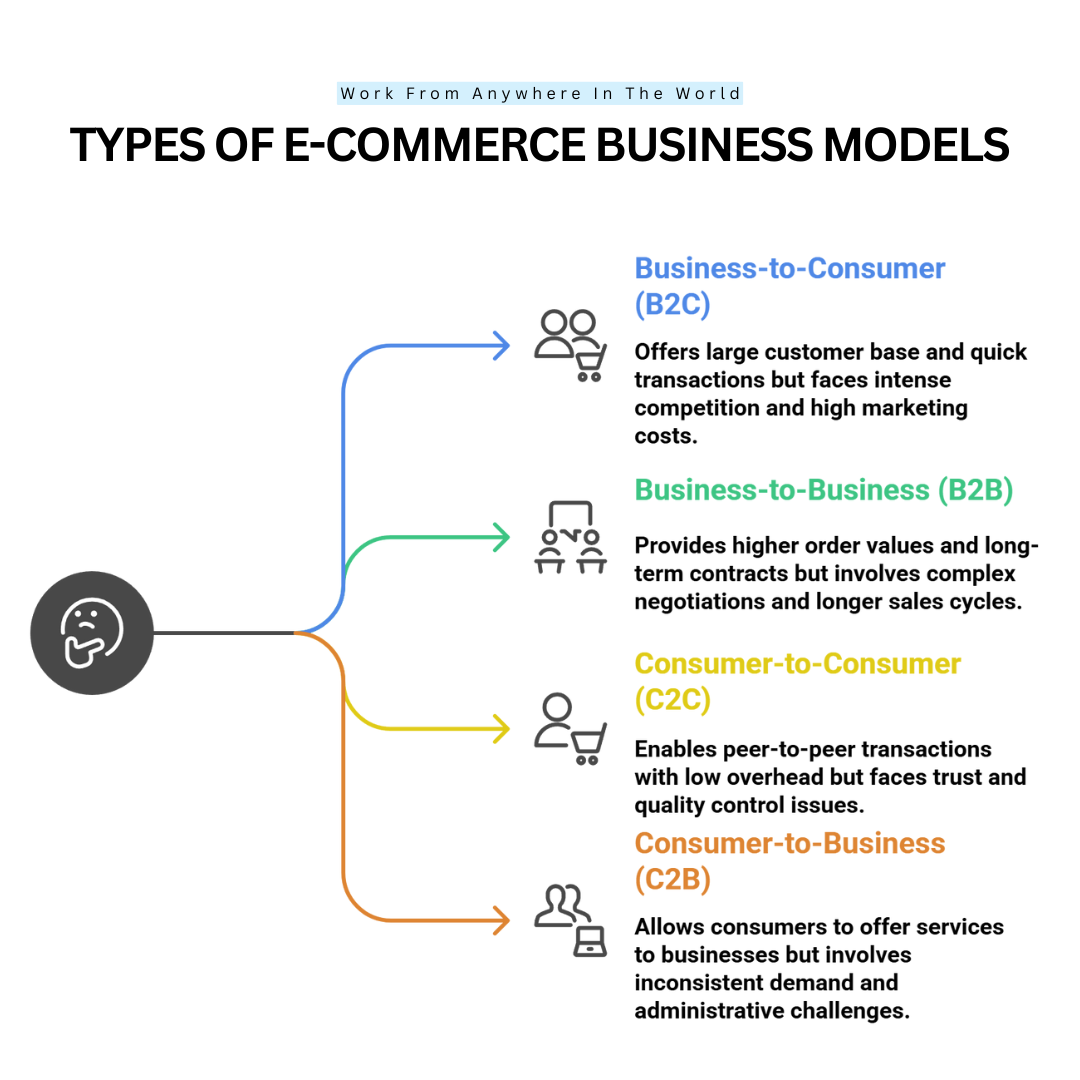
1. Business-To-Consumer (B2C)
Businesses selling goods or services directly to customers are known as business-to-consumer (B2C) e-commerce. This model, which covers sectors including grocery, electronics, and fashion, is the most widely used.
Pros
B2C businesses benefit from a large, diverse customer base, providing significant revenue potential. Transactions are typically quicker than B2B, allowing faster cash flow and scalability.
Digital marketing tools make targeting specific audiences more efficient, enhancing customer engagement and brand loyalty. E-commerce platforms enable easy global reach, reducing geographical limitations.
B2C models encourage innovation in product development and service delivery, responding rapidly to consumer trends. Personalized experiences and loyalty programs strengthen long-term customer relationships.
Social proof and reviews can drive sales. Overall, B2C offers dynamic growth, brand recognition, and opportunities for creative marketing strategies.
Cons
B2C businesses face intense competition, requiring constant differentiation and marketing investment. Getting new clients can be expensive, especially in markets with high competition.
Consumer expectations for fast delivery, excellent service, and seamless digital experiences put pressure on operations. High return rates and complaints can affect profitability.
Marketing campaigns must be ongoing to maintain visibility and engagement. Seasonal demand fluctuations can create inconsistent revenue streams. Managing large volumes of small transactions increases operational complexity.
Data privacy and cybersecurity are crucial, as breaches can damage reputation. Profit margins may be lower than B2B, necessitating volume-driven strategies for sustainable growth.
2. Business-To-Business (B2B)
B2B e-commerce focuses on transactions between businesses, such as manufacturers selling to wholesalers or SaaS companies serving enterprises.
Pros
B2B businesses often enjoy higher order values and long-term contracts, providing predictable revenue and financial stability. Marketing costs are generally lower compared to B2C, as targeting specific companies is more focused.
Strong client relationships encourage repeat business and referrals, fostering loyalty and trust. B2B transactions allow for customized solutions, increasing value and client satisfaction.
Negotiations and partnerships often lead to mutually beneficial collaborations. Sales teams can leverage industry expertise to create strategic advantages.
Overall, B2B offers sustainable growth, lower customer churn, and opportunities for high-value contracts, making it ideal for businesses seeking stability and long-term profitability.
Cons
B2B sales cycles are typically longer, requiring patience and strategic planning. Negotiations can be complex, involving multiple stakeholders and legal considerations.
Securing new clients often demands personalized approaches and extensive relationship-building. Market size may be smaller than B2C, limiting the pool of potential customers.
Businesses must maintain high service levels and technical expertise to retain clients. Dependence on a few large clients can increase risk if contracts are lost.
Marketing strategies require specialized knowledge and can be less flexible than B2C campaigns. Overall, B2B involves higher operational complexity, slower revenue generation, and significant effort to maintain strong client relationships.
Wealthy Affiliate – Mini Review (2025)
If you’ve ever thought about turning your blog, passion, or niche into an online business,
Wealthy Affiliate (WA) is one of the most beginner-friendly platforms I’ve used.
It combines step-by-step training, website hosting, SEO research tools,
and an active community all in one place.
What I like most: you can start free (no credit card needed),
explore lessons, test the tools, and connect with other entrepreneurs
before upgrading. WA isn’t a “get rich quick” scheme — it’s a platform where success comes
from consistent effort and applying what you learn.
3. Consumer-To-Consumer (C2C)
C2C platforms are a key example of e-commerce business models, enabling peer-to-peer transactions through online marketplaces.
Pros
C2C platforms empower individuals to sell products or services directly to other consumers, creating a flexible, low-cost marketplace. Users can monetize unused items, reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
Transactions are often simpler and faster, facilitated by online marketplaces and apps. C2C encourages peer-to-peer engagement, fostering community connections and trust through reviews and ratings.
Sellers can reach a global audience without significant overhead, while buyers gain access to unique or second-hand products at competitive prices.
Overall, C2C offers accessibility, convenience, and economic opportunities for individuals, promoting entrepreneurial activity without the need for formal business infrastructure.
Cons
C2C platforms face challenges with trust and reliability, as users may encounter fraud or misrepresentation. Quality control is inconsistent, and disputes between buyers and sellers can be complex to resolve. Payment and shipping logistics can create delays or complications.
Limited legal protections may leave consumers vulnerable if transactions go wrong. Market saturation can make it hard for sellers to stand out. Customer support is often minimal compared to traditional businesses.
Additionally, C2C businesses must rely heavily on platform policies and fees, which can impact profitability. Overall, C2C carries risks of fraud, inefficiency, and variable customer experiences.
4. Consumer-To-Business (C2B)
In C2B e-commerce, individuals sell products or services to businesses. This includes freelancers, influencers, and user-generated content platforms.
Pros
C2B models allow consumers to offer products, services, or content directly to businesses, creating unique monetization opportunities.
Freelancers, influencers, and content creators can reach a wide range of clients without intermediaries. Businesses gain access to diverse talent and innovative solutions at competitive prices.
This model promotes flexibility, creativity, and niche specialization, allowing individuals to leverage skills or assets for income.
C2B also encourages personalized collaborations, fostering mutually beneficial relationships. Platforms facilitating C2B transactions streamline payments, contracts, and project management.
Overall, C2B empowers consumers as service providers while giving businesses cost-effective access to expertise, creativity, and market insights.
Cons
C2B arrangements can involve inconsistent demand, making income unpredictable for consumers. Competition among individuals offering similar services can drive prices down, affecting profitability.
Businesses may face challenges in quality control and ensuring reliability when dealing with multiple independent contributors.
Legal, tax, and contractual considerations can complicate agreements. Payment delays or disputes may arise, especially without robust platform protections.
Scaling operations is difficult for consumers acting as solo providers. Marketing and self-promotion are essential but time-consuming for individuals.
Overall, C2B carries risks of income instability, competitive pressure, and administrative challenges for consumers, while businesses must manage quality, trust, and contractual complexities.
Based On Revenue Models
1. Retail E-Commerce (Direct Sales)
Retail e-commerce through direct sales is a prominent example of e-commerce business models, providing businesses with complete control over sales, branding, and customer interactions.
Pros
Direct retail e-commerce offers complete control over product presentation, pricing, and marketing strategies, enhancing brand identity. Businesses can build direct relationships with customers, fostering loyalty and personalized experiences.
Eliminating intermediaries increases profit margins and allows faster feedback on product performance. Online stores operate 24/7, providing convenience for customers and continuous revenue potential.
Analytics tools help track behaviour, optimize campaigns, and improve inventory management. Global reach enables access to a larger market without geographical constraints.
Direct sales encourage faster innovation cycles, flexibility in promotions, and the ability to respond quickly to trends. Overall, it maximizes profitability, engagement, and brand control.
Cons
Retail e-commerce direct sales require significant investment in website development, digital marketing, and logistics. Businesses must handle inventory management, order fulfillment, and customer service internally, increasing operational complexity.
Competition is intense, demanding constant optimization of pricing, promotions, and user experience. Technical issues, cybersecurity threats, and website downtime can negatively impact sales and reputation.
Attracting traffic requires ongoing marketing effort, including SEO, social media, and paid ads. Returns and refunds management can be costly and time-consuming. Scaling operations involves more staff and infrastructure.
Overall, while profitable, direct retail e-commerce demands careful planning, resources, and continuous attention to maintain efficiency and customer satisfaction.
2. Dropshipping
Dropshipping is an e-commerce model where sellers list products without holding inventory, relying on suppliers to ship directly to customers.
Pros
Dropshipping minimizes upfront investment since no inventory purchase is required, reducing financial risk. Sellers don't have to pay for storage to provide an extensive range of goods.
The model allows for flexible location and scalability, as operations can be managed from anywhere with an internet connection. It simplifies logistics, as suppliers handle storage, packing, and shipping.
Marketing and customer engagement remain the primary focus, enabling entrepreneurs to test products and niches quickly. Additionally, it supports rapid expansion into global markets without significant operational overhead.
Overall, dropshipping offers low-risk entry, operational flexibility, and diverse product opportunities for online entrepreneurs.
Cons
Dropshipping has lower profit margins due to reliance on suppliers and high competition in popular niches. Quality control is limited, increasing the risk of defective products or delayed shipments, which can harm the reputation.
Sellers are dependent on supplier reliability, leaving little control over inventory or fulfillment. It gets harder to handle customer service problems like refunds and complaints.
Shipping times can be longer, especially with international suppliers. Marketing costs can be significant to generate traffic and sales.
Overall, dropshipping requires careful supplier selection, constant oversight, and strong marketing strategies to maintain profitability and customer satisfaction.
3. Subscription E-Commerce
One kind of creative e-commerce business concept that increases customer convenience and loyalty while producing recurring income is subscription services.
Pros
Subscription e-commerce ensures predictable, recurring revenue, which helps with cash flow and financial planning. It strengthens customer loyalty through regular engagement, creating long-term relationships and reducing churn.
Companies can collect valuable consumer preference data, which enables focused marketing and customized products. Inventory and demand planning become more efficient due to predictable purchase patterns.
Subscription models often allow for premium pricing and exclusive products or experiences, increasing customer lifetime value. Marketing costs can be lower as retention is prioritized over constant new acquisition.
Overall, subscription e-commerce promotes stability, customer satisfaction, and sustainable growth with consistent revenue and brand engagement.
Cons
Subscription e-commerce requires constant effort to maintain customer satisfaction, as cancellations can quickly impact revenue.
Acquiring subscribers can involve high initial marketing costs. Businesses must manage inventory, logistics, and timely delivery consistently to avoid dissatisfaction. Personalization and variety are necessary to prevent subscriber fatigue or churn.
Technical systems for recurring billing, customer management, and payment security add complexity and costs. Competitors offering similar subscriptions can make differentiation challenging. Additionally, customer retention depends heavily on product quality, service, and perceived value.
Overall, while profitable, subscription e-commerce demands continuous innovation, operational precision, and marketing investment to sustain long-term subscriber loyalty.
4. Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketing is a popular example of e-commerce business models, enabling individuals and businesses to earn commissions by promoting products online.
Pros
Affiliate marketing requires minimal startup costs, making it accessible to individuals and small businesses. There’s no need to create products, manage inventory, or handle customer service, reducing operational complexity.
It offers passive income potential, as earnings can continue from past promotions. Affiliates can leverage blogs, social media, and email marketing to reach broader audiences.
Performance-based commissions incentivize results, allowing scalability without fixed costs. Businesses benefit from expanding their reach and driving sales through affiliate networks.
Analytics tools help optimize campaigns and track conversions. Overall, affiliate marketing provides low-risk income opportunities and flexible growth for both affiliates and merchants.
Cons
Due to intense competition, affiliate marketing makes it difficult to stand out and make a sizable profit. Earnings are often unpredictable and depend on conversion rates, traffic quality, and seasonal demand.
Affiliates have limited control over product pricing, availability, or quality, which can impact commissions. Dependence on third-party programs and changing terms of service poses risks.
It takes time and regular content creation to gain an audience's trust. Marketing strategies require ongoing effort, SEO knowledge, and social media engagement.
Additionally, fraudulent clicks or unethical practices in affiliate networks can reduce income. Overall, affiliate marketing demands patience, persistence, and strategic promotion to succeed.

Based On Product Types
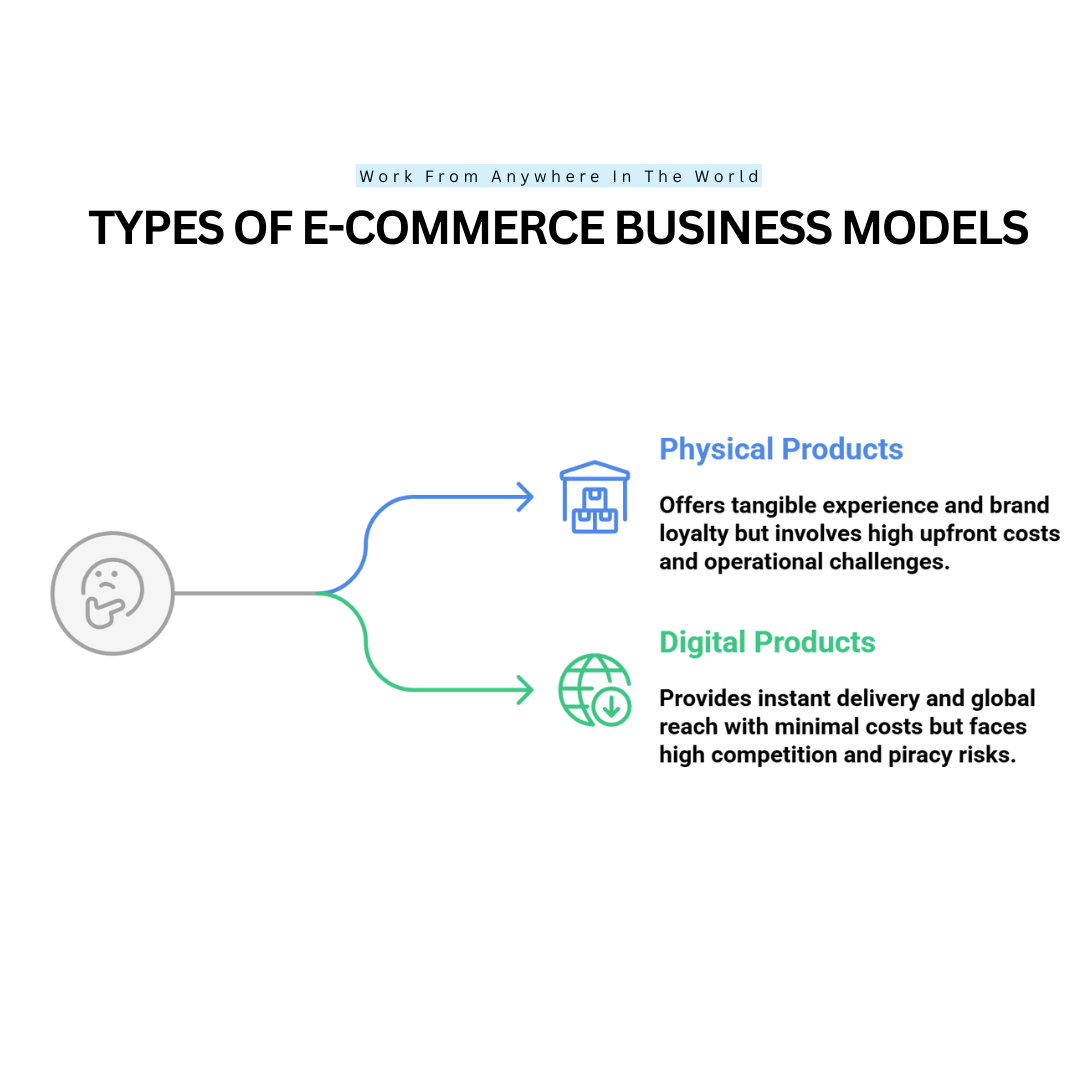
1. Physical Products
Selling physical products is a traditional approach within e-commerce business models, involving inventory management, production, and direct distribution to customers.
Pros
Physical products provide a tangible experience, which can enhance customer satisfaction and brand loyalty. They can be differentiated through quality, design, and packaging, creating strong market positioning.
Businesses can leverage retail, e-commerce, and wholesale channels for diverse sales opportunities. Physical products often allow higher perceived value, enabling premium pricing.
Inventory management and production scalability can support growing demand, while repeat purchases encourage long-term revenue. Tangible goods also facilitate promotions, bundling, and physical presence at events or stores.
Overall, physical products create lasting customer impressions, tangible brand identity, and opportunities for consistent revenue through multiple distribution channels.
Cons
Physical products involve significant upfront costs for manufacturing, inventory, and storage. Logistics, shipping, and handling complexities increase operational challenges and expenses. Unsold inventory risks tie up capital and may result in losses.
Quality control, returns, and customer service management are essential to maintain a reputation. Market trends and demand fluctuations can make forecasting difficult.
Physical products require marketing investment to compete effectively against similar offerings. Scaling operations often necessitates more staff, warehousing, and distribution resources.
Overall, while profitable, selling physical products demands careful planning, financial investment, and operational management to ensure efficiency, customer satisfaction, and sustainable growth.
2. Digital Products
Offering digital products is a modern strategy within e-commerce business models, providing instant delivery, global reach, and scalable revenue opportunities.
Pros
Digital products have minimal production and distribution costs, as they require no physical inventory or shipping. They can be sold globally with instant delivery, increasing market reach and scalability.
Updates and improvements can be implemented easily without recalling products. Automation allows for passive income, with sales occurring 24/7.
They enable niche targeting and personalized offerings, enhancing customer satisfaction. Marketing and distribution can be highly efficient through online platforms, email, and social media.
Overall, digital products offer low overhead, high scalability, and continuous revenue potential while providing customers with immediate access and convenience.
Cons
Digital products face high competition due to low barriers to entry, making differentiation essential. Piracy and unauthorized distribution can reduce revenue and affect intellectual property rights.
Continuous updates, technical support, and customer service are necessary to maintain quality and satisfaction. Marketing requires ongoing effort to drive traffic and conversions in crowded online markets.
Refund policies and payment processing issues can complicate sales. Technical failures, such as server downtime or software bugs, can harm the reputation overall.
At the same time, profitable and scalable, digital products demand careful attention to security, marketing, and customer support to ensure consistent revenue and long-term success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, e-commerce business models—B2C, B2B, C2C, C2B, subscription services, dropshipping, and white or private labelling—offer diverse opportunities for entrepreneurs.
Each model presents unique advantages, from scalability and recurring revenue to global reach and low startup costs, alongside challenges like competition, operational complexity, and quality control.
Choosing the right model depends on resources, target audience, and long-term goals. Understanding these models enables businesses to strategically plan, optimize revenue, and deliver value while navigating the dynamic digital marketplace effectively.
I trust you enjoyed this article on The Ultimate Guide To E-Commerce Business Models. Please stay tuned for more insightful blogs on affiliate marketing, online business, and working from anywhere in the world.
Take care!
— JeannetteZ
💬 Your Opinion Is Important To Me
Do you have thoughts, ideas, or questions? I’d love to hear from you. Please leave your comments below or email me directly at Jeannette@WorkFromAnywhereInTheWorld.com.
📚 More Work From Anywhere Reads
🚀 Ready to Build a Business You Can Run from Home
or from Anywhere in the World?
Imagine creating income on your terms — from home, a cozy café, or wherever life takes you.
With the right tools, training, and community support, it’s entirely possible.
Start your own online business for free — no credit card needed.
Disclosure
This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate and participant in other affiliate programs, I earn from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you. Please read my full affiliate disclosure.